Tekstitykset
Have you ever wondered how your phone
manages to know what direction you are holding it? It's using a device called an
accelerometer. It works by sensing the acceleration of gravity and then you can calculate what
direction the phone is facing. But how does a piece of electronics sense something mechanical like
acceleration? The answer is MEMS. Microelectromechanical systems. MEMS are
kind of like silicon integrated circuits but they are mechanical in nature. MEMS
manufacturers use similar techniques that are used to make electronics but instead they're making tiny
mechanical structures that can interface to electronics... allowing you to build some interesting
things. Here I've got some MEMS dies that I made out of silicon. They contain a lot of the same basic
structures that you might find in a modern MEMS chip. Let's take a look under the microscope.
This is a tiny resistor. The lighter colored material is actually
electrically conductive silicon and this darker area that's been etched
away doesn't conduct. This long winding electrical path forms
a resistor, very similar to how long pieces of wire
would also have a significant resistance. So if you made an electrical connection
between these two points you'd have a microscopic resistor. Now in
order to understand how an accelerometer works, let's look at a MEMS capacitor. It doesn't
look like a capacitor does it? Well remember that all a capacitor really is is two conductive plates that are
electrically separated. Here are the two terminals of the
capacitor. Over here we have what's called a combed finger arrangement. The two structures are very close to
each other but they aren't quite touching. Let me
highlight it for you. Now it should be more obvious that you have
parallel surfaces which form a capacitor. But this is no ordinary capacitor! It's a
physical structure that can move. This thing over here is basically a tiny
weight made out of silicon and it's kind of like a suspended mass
on the end of a spring. Movement, vibrations, and even gravity can
cause this little mass to move around and when it does it shifts the entire
combed finger structure. When the fingers move the distance
between the fingers changes. And when the distance between the
fingers changes, you get a change in capacitance. So now
we have an electromechanical system that can sense movement and turn it into a changing capacitance
value. The next step would be to design circuitry that can sense the change in
capacitance and convert it into useful voltages or
serial data but that's beyond the scope of this
tutorial. A modern MEMS accelerometer will contain structures similar to this except with even more fingers to
increase the surface area which increases the capacitance which
makes changes in acceleration easier to detect. Here's another
electromechanical capacitor except it senses acceleration on the
horizontal axis. (Ignore this. That will right buff out.) When
the suspended mass moves in the horizontal direction, the surface area between the fingers
changes and then you can have some electronics to sense the change in
capacitance again. Now if you want to play around with
accelerometers at home, you don't need a microscope. You can go
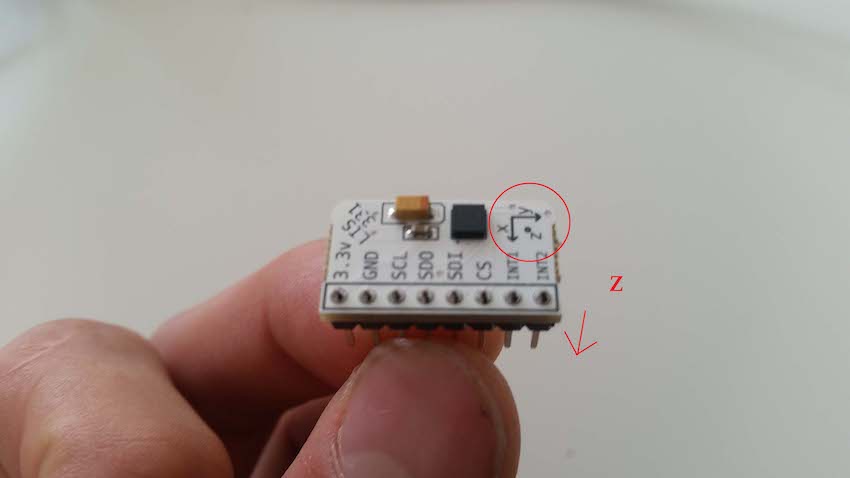
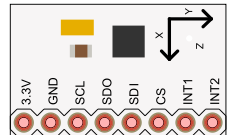
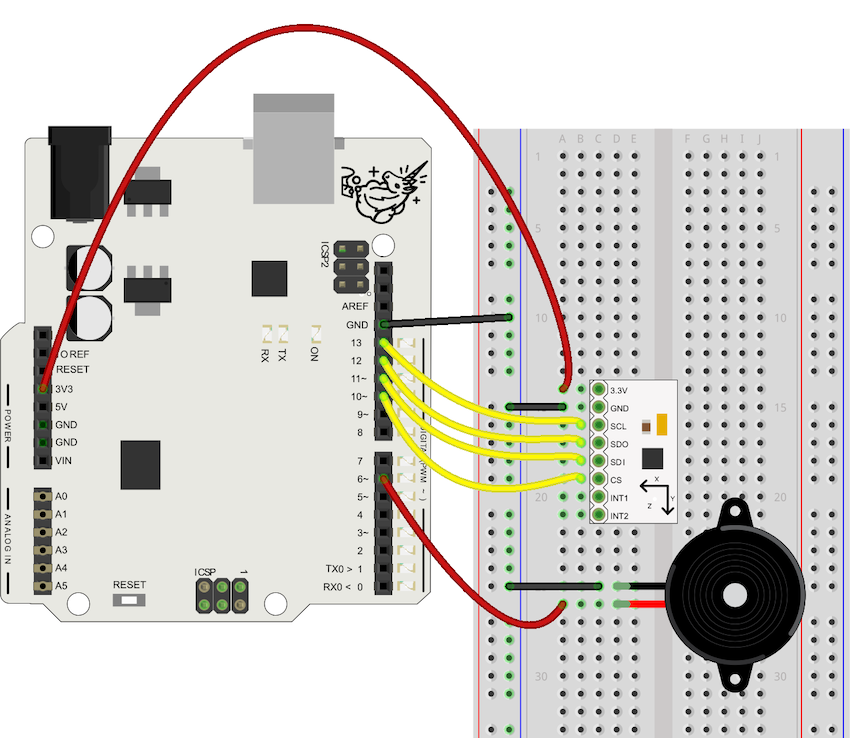
to a company like Adafruit and buy a PCB with an accelerometer chip on
it. Just power it with 5 volts between Vin and ground and you'll get voltages that correspond
to acceleration on the X, Y and Z axes. Now you know how an accelerometer works
thanks for watching!